Close
CHAPMAN STONE AGAR 500 grams/bottle
SKU
CDL/1017
Brand
CONDALAB
Pre-order (Deliver in 8 to 12 weeks)
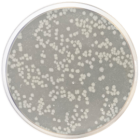
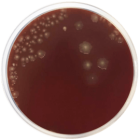
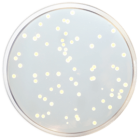
Champan Stone Agar is used for the isolation of pathogenic Staphylococci in foods. It is similar to Staphylococcus N° 110 Agar (Cat. 1032), but contains ammonium sulfate to detect the gelatinase activity (Stones reaction), and sodium chloride concentration is reduced to 5,5%.
The main modification of this medium is the inclusión of ammonium sulfate that allows the direct observation of gelatin hydrolysis instead of adding reagents to the plate medium. Due to the presence of ammonium sulfate in the medium itself, there is no need to flood the plate with the ammonium solution to detect the gelatin liquefaction (Stones method). Ammonium sulfate precipitates unhydrolysed gelatin, so a transparent halo will appear around the gelatinase (+) colonies.
Casein peptone provides nitrogen, vitamins, minerals and amino acids essential for growth. Yeast extract is a source of vitamins, particularly of the B-group. D-Mannitol is the fermentable carbohydrate providing carbon and energy. Sodium chloride, in high concentrations, inhibits most bacteria except Staphylococci. Gelatin is a protein derived by the hydrolysis of collagen, found abundantly in bones, skin, tendons, cartilage and animal tissue. It is used in culture media to determine gelatinolysis by bacteria. The gelatinoses produced by the microorganisms hydrolyze the gelatin liquefying a solid medium or preventing the gelation of a medium containing gelatin. Bacteriological agar is the solidifying agent.
The staphylococcal colonies are yellow, yellow-gold or orange, ferment mannitol, coagulase-positive, produce beta-hemolysis in media such as Blood Agar (Cat. 1108) and are gelatinase-positive (positive Stone´s reaction). Any pigmented colony (yellow or soft orange) that is surrounded by a clear zone is probably a pathogenic Staphylococcus. Pale colonies, practically lacking in color or not producing pigment, should not be considered as positives, even if they are surrounded by a clear zone (halo), and are presumptively identified as S. epidermidis colonies.
It is recommended to pick the colony and inoculate it in 0,1-0,2 ml of Brain Heart Infusion Broth (Cat. 1400) and perform the coagulase test. At the same time, add a drop of Bromocresol purple to the colony site in order to determine mannitol fermentation: a yellow color formation is a positive reaction. The zones of clear halos around the colonies indicate degradation by the enzyme gelatinase (gelatin hydrolysis).
| Brand | CONDALAB |
|---|
Write Your Own Review
More from CONDALAB












Validate your login